リサイクルプラント運営事業
近赤外線を用いた選別技術で、回収したLIMEXと汎用プラスチックを自動選別し、再生利用する世界初のプラントを運営しています。 2022年11月竣工の横須賀サーキュラー工場は国内最大級の規模を有し、同様の工場を国内外に展開予定。脱炭素社会、循環型社会に向けてマテリアルリサイクルを通じた資源循環モデルを推進します。
横須賀サーキュラー工場
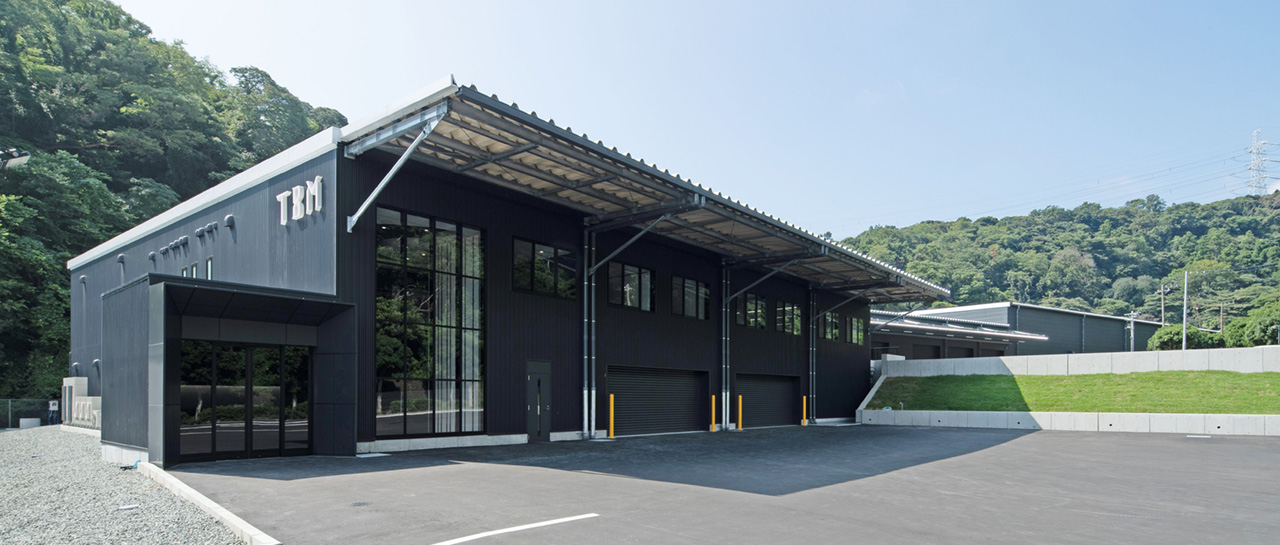

- 敷地面積
- 13,693㎡
- 建物床面積
- 7,859㎡
- 引受量
- 年40,000t
- 生産量
- 年24,000t
- 所在地
- 神奈川県横須賀市神明町58-9
横須賀サーキュラー工場の特徴
LIMEXと汎用プラスチックを自動選別し、再生利用する世界初のプラント
海外の大手選別機メーカーと連携し、近赤外線による素材検知・選別の検証を進め、
プラスチックや紙などの他素材から LIMEXのみを自動選別する独自のプログラムを開発。
プラスチックのマテリアルリサイクルプラントとして国内最大級
本工場が備える年間約4万トンの処理能力、年間約2万4000トンの再生ペレットの生産能力は、
プラスチックのマテリアルリサイクルのプラントとしては国内最大級の規模。
家庭由来の容器包装プラと製品プラの一括回収、再生に先駆的に着手
プラ新法が施行され、家庭から出る廃プラスチック全般を一括回収する新たな分別区分
「プラスチック資源」に対応したリサイクルのシステムが求められる中、
本工場では、家庭から排出される雑多な廃プラスチックを選別、再生することが可能です。
焼却処理されてきた雑多な事業系の廃プラスチックを再生する先進性
自動選別ラインの導入により、これまで焼却処理されていたオフィスや工場などから排出される
雑多な事業系の廃プラスチックなども積極的に受け入れ、再生することが可能となります。

横須賀サーキュラー工場では、「横須賀市ゼロカーボンシティ」を宣言している横須賀市と連携し、
使用済みのLIMEXや廃プラスチックのマテリアルリサイクルする実証実験を進めています。
リサイクルプラント運営の拡大戦略
-
1. 容器包装リサイクル協会ルート
複数の地方行政と容リ協会を介した間接有価引受契約を獲得
令和5年度13,290t 強 -
2. 大臣認定ルート(プラ新法)
横須賀市から直接有価引受契約を獲得 -
3. 産業廃棄物プラスチック
産業廃棄物プラスチック拠出者から直接有価引受契約を随時獲得(不動産開発会社等) -
4. 産業由来単一プラスチック
工場端材等の単一プラの有価買取
TBMにて再ペレ化して販売を企図
モデルケースとして国内外へ横展開
家庭から排出される使用済LIMEXと汎用プラスチックを一括回収し、工場内で自動選別してそれぞれ再生ペレットを製造する横須賀サーキュラー工場をモデルケースとして、廃プラスチックの処理を焼却・熱回収に頼る国内各エリアに拡大していきます。また、家庭におけるプラスチック分別の仕組みが未発達な海外エリアに対しても、リサイクルシステム構築の解決策として本スキームを展開していく計画です。
マテリアルリサイクルプラントが求められる背景
伸びないマテリアルリサイクル率
2021年の日本のプラスチックのマテリアルリサイクル率は21%で、サーマルリカバリー率は63%+単純焼却8%。2006年の容器包装 リサイクル法の改正に伴い、サーマルリカバリーの比率が伸びている。なお、EU推計(2021年)によると、 EU27カ国のプラス チック包装の廃棄物のマテリアルリサイクル率は平均39.7%。
参考:「プラスチックリサイクルの基礎知識 2023」(プラスチック循環利用協会) 「EU packaging waste generation with record increase」(2021年、Eurostat :EU統計局)廃プラスチックの資源価値向上が課題
一般廃棄物のうち、容器包装リサイクル法に基づくルート等を通じて回収された PETボトル及びプラスチック製容器包装や、産業廃棄物の廃プラスチックの生産・加工ロスなどは分別回収・リサイクルが進んでいるが、それ以外の廃プラスチックは資源価値に応じた市場が十分に形成されていないため、分別回収のインセンティブが低く、価値が低い廃プラスチックと混合されることで本来価値の高い廃プラスチックもサーマルリカバリーに回されることが多い。これに向けては、廃プラスチックの資源価値に応じた効率的な分別回収・選別(ソーティングセンターの設置等)の実施により、リサイクルされる廃プラスチック量を向上させることが求められる。また、プラスチック資源循環促進法に基づくプラスチック使用製品設計指針を踏まえた環境配慮設計や、自主回収による高品質な廃プラスチックの確保、容器包装と製品プラスチックとの一括回収等による経済合理性の高いリサイクルの推進が求められる。 「成長志向型の資源自律経済戦略」(2023年、経済産業省)